OET Score Calculator Guide – Check Your Grade
- 120 Comments

The Occupational English Test (better known as OET), is a testing system designed to measure the English language competency of healthcare professionals who intend to move to and register in English-speaking countries.
Table of Contents
The test looks at the abilities of candidates in four areas – speaking, writing, reading, and listening – to assess their overall English ability, although it is of course tailored for candidates who work in the various fields of healthcare.
Until August, 2018, OET candidates were assigned grades ranging from E-A; however, a new scoring system has been implemented that assigns candidates a numerical grade, ranging from 0-500.
OET Grading
Since September, 2018, the OET has been graded on a scale of 0-500 for each of the four sections, which are known as “subtests”. The highest possible score is 500, and the lowest is 0, as can be seen from the following table:| OET | IELTS BAND EQUIVALENT | LEVEL OF ENGLISH | |
| OET SCORE | OET GRADE | ||
| 450-500 | A | 9 | High level of proficiency in the language. Able to communicate fluently and accurately. Can understand written or verbal discourse with ease. |
| 8.5 | |||
| 8 | |||
| 350-440 | B | 7.5 | Able to communicate effectively although some inaccuracies or hesitations may occur which do not impede communication. |
| 7 | |||
| 300-340 | C+ | 6.5 | Able to communicate adequately despite occasional errors. |
| 200-290 | C | 6 | Able to understand standard input but may require clarification on higher level language. |
| 5.5 | |||
| 100-190 | D | 5 | Able to interact and understand simple and routine tasks but may require clarification. Errors frequently occur, causing strain in communication. |
| 4.5 | |||
| 4.0 | |||
| 0-90 | E | 0-4 | Able to understand familiar and basic phrases. Can interact only if the other person is prepared to clarify information. |
This grading system allows for healthcare programs around the world to ensure the English levels of prospective employees. As can be seen from this table, a score of 350 or higher indicates the sort of ability that would be desired by most healthcare systems.
Disclaimer: The calculator above is only an estimation based on the premise of 30 marks out 42 to be 350.
Step 1
Step 2
Disclaimer : Take note that this is a general guide and you still need to check your eligibility with the respective registration bodies.
Test Format and Marking
OET is 3 hours long approximately. The structure of the test looks like this:| Subtest | Duration | Content | Requirements |
| Listening | 40 minutes | 2 parts | Candidates must understand a range of spoken materials, including patient consultations and lectures. |
| Reading | 60 minutes | 2 parts | Candidates must read and understand different types of written healthcare-related materials. |
| Writing | 45 minutes | 1 part | Candidates must write a letter clearly and accurately for a reader. *This is specific to the candidate’s field of occupation. |
| Speaking | 20 minutes | 2 parts | Candidates must communicate effectively in a role-play situation. *This is specific to the candidate’s field of occupation. |
OET examines candidates’ abilities in speaking, writing, listening, and reading. As such, there are four separate subtests, one for each of these areas. The two receptive skills – reading and listening – are intended to determine how well a candidate can understand written and spoken English in a medical capacity. These two tests are the same regardless of a candidate’s occupation. This is different for the writing and speaking tests, which are specific to each of the occupations covered by the OET.
OET Preparation Material for Nurses , OET Preparation Material For Pharmacy and OET Preparation Material for Doctors are essential resources to prepare effectively for the exam.
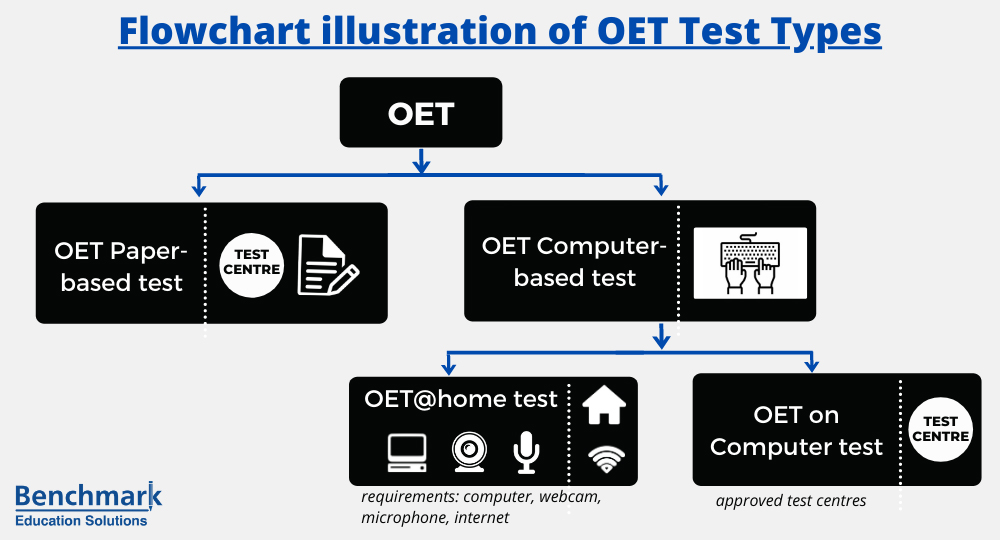
OET Test Types
OET now comes with two different formats- Paper Based
- Computer-based
- 2.1 OET at home
- 2.2 OET on Computer @ test venue

Reading and Listening
The listening and reading subtests are marked by OET examiners at the testing center. They will be randomly and anonymously assigned in order to prevent any sort of cheating. The examiners are required to strictly follow a guide that tells them how to mark your answers and calculate your score.
Part B and C of the reading test are handled differently: It is marked by a machine, which reads data from the paper after it is scanned. The whole system is closely monitored to ensure fairness and accuracy. In listening and reading, you are assessed for various skills in each part of the subtests. The scores based of tested skills are listed in the table below:
| S. no | Listening | Reading |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Part A: 24 questions 2 Recordings (12 questions each) Notes completion Skills: It tests your ability to listen for details, comprehend, and interpret accurately. | Part A: 20 questions 1-7 Matching Questions. 8-20 Fill in the blanks. Skills: It requires you to quickly scan the text, locate relevant information and record specific information. |
| 2 | Part B: 6 questions 3 option MCQs Skills: It is assessed for listening to find gist, or identifying a speaker's opinion, attitude, or purpose to decide what will be the outcome of each conversation. | Part B: 6 questions (6 workplace extracts) 3 option MCQs Skills: It tests you for identification of main ideas, purpose and recognition of important details. |
| 3 | Part C: 12 questions 2 Recordings (6 questions each) 3 option MCQs Skills: It tests your ability to follow extended conversations to understand gist, main idea, and opinion | Part C: 16 questions 2 long texts 4 option MCQS questions Skills: It tests your ability to comprehend the explicit and implicit meaning of the author. It also tests your ability to understand the contextual meaning of specific vocabulary. |
Speaking and Writing
The audio files from the speaking test and the written papers from the writing test will be collected and randomly assigned to examiners for grading. These will be re-checked in order to ensure that a fair grade has been assigned. A particularly strict examiner may have their grading system altered to bring it more in line with OET standards. A consensus is required from the two (or more) examiners who look at a speaking or writing test in order for the grade to be accepted and published by the OET center. You may well ask how the speaking and writing tests are assessed. In other words, what are the examiners looking to hear or read from the candidates? The criteria are somewhat similar, with a few differences. They are listed in this table:| S. No | Writing | Speaking |
| 1. | Task has been completed. | Communication was effective. |
| 2. | Appropriate language used. | Speech was intelligible. |
| 3. | Understood the material. | Spoke fluently. |
| 4. | Grammatically accurate. | Appropriateness. |
| 5. | Spelling, punctuation, etc. | Grammar and other resources used well. |



















In OET reading how much questions need to correct for minimum C+
In listening how much qusestions need to correct for minimum B grade
65%
And how many questions are needed to be right to get the minimun B grade for the reading part of the test? Thank you!! 🙂
65%
what about listeing? how much minimum correct answers we need to achieve 350+ score
at least 30.
I have scored only 260 for oet writing,however,im very clear that it was error free letter and only added relevent informations.I wonder how i scored very less mark
you might have written an error-free letter, but there could be mistakes in overall understanding of the scenario. It makes more sense to start practicing again considering significant progress needs to be made to reach 350: OET Writing Correction
in my first sitting i got L-380 R-370 W-300 S-330
on my 2nd i got L-370 R-310 W-350 S-320
would i still make it to Uk if i combine this scores? thanks for the answer
if i had a score pf 32 out of 42 question in reading would that give me a B, that’s 350 and above
Possibly, but we recommend visiting official OET website as our calculator is only an estimation.
I got 310 in listening but other module 350, 360, 370.
What i can do ?
Take the test again.
Do I need to take the whole test again?
Yes, but contact your registration agency for confirmation.
What is the equivalent total score of 65% for reading and listening? Or how many correct answers should I achieved in order to pass the reading& listening part? Thanks
Hello how much marks out of 42 do we need to get a B in Reading
Hi .what will be eligibility score for nurses in oet test, And also i would like to know how they are calculating the score.
You need 350 out of 500 in order to pass. Use this calculator
I got speaking 340, writing 260, listening 350, and reading 270..please advise what to do.. tnx
Start preparing again! Use these services:
OET Writing Correction
OET Reading Practice
I think I included all the tasks however I had an error understanding the date the patient has to be discharged, how is that usually graded? is that already just a C? Thanks
Not sure which scenario you are referring to. Yes, it’s important to write the discharge date accurately. You will lose some marks for reporting wrong information.
Thanks for replying. The query was about the recent oet exam. i just wanted to know how high is the possibility that I am getting a C instead of a B, because of the date error I made.
As mentioned, one mistake cannot necessarily lead to C grade, you might lose 10 points at worst
My oet exam is on 30th august, would it be on old criteria or new on for writing?
New critieria: OET Test Date
What about reading? How many correct answers we need to achieve a B score in oet
What about listening?for achieving a B grade, how many answers to be corrected?In 42 questions?
Is it possible to resit for one module? And which all countries accepted resiting
Thanks
In most of the cases, one needs to sit for all 4 modules again, but check with your assessment authority and find out what they require
For c plus in listening and reading how many questions to be corrected
If I got one subset C+ and the rest are all B, do I need to retake only that C+ or retake all ?
Is to get at least B in all subset in one setting?
In most of the cases, one needs to sit for all 4 modules again, but check with your assessment authority and find out what they require
How many questions should be correct in listening and reading test in order to score grade A? I mean out of 42 .
How many question you need to get right to get OET a grade in listening and reading
If I get 2 B’s and 2 C+, do I have to rewrite the tese
You might have to. Most of the registration bodies require all B. Check with your registration body first.
Will you offer the case notes for us in writing correction?
Yes. At the same time, you are free to use your own case notes as well.
Hi I got 340 in listening. What I need to do now.please guide me.
Could you please provide the ratio of grade / score and how many correct answers should take for each modules..
OET Score Calculator
how many questions out of 42 should be corrected in listening module of OET to get 350+ marks?
Use this OET Score Calculator
hey i need a minimum of 350 in all my modules. how many wrong answers can I have and still achieve that score in reading and listening ?
Use this link: OET Score Calculator
If the case is not urgent case, and I able to emphasize that in the introduction but mistakenly on the conclusion I requested the specialist urgent assessment, definitive diagnosis and emergency management. Do I will lose marks for it?
I was about to correct it but the time couldn’t allow me to do so. How I will be graded for it
Yes, it’s not ideal to seek urgent action when the case notes do not include such request. However, there is nothing to be worried about as the examiners look at all the parameters before awarding a score.
the confusing point was the medical presentation considered as emergency, and one of the diseases needs an emergency intervention like fever or convulsions and so on but after I wrote the hall letter I found that they mentioned in the case notes the case is not urgent, so I able to update the introduction accordingly but when I came to the conclusion the time was up
there isn’t much to worry about. your letter can still sail through without much difficulty.
Hi,
I would be thankful if you inform me of the harder subtest according to the scoring perspective.
This is very subjective. However, majority of the test takers find OET writing to be more challenging than the rest.
hi, i want to ask if how much is my over all score in my oet if i had 300 in my writing, 420 in my listening, 350 reading and 390 speaking?
Unlike IELTS, there is no concept of an overall score the OET. If you are looking for B grade in all 4 modules, then you might need to book another exam as 300 is C+.
can I remark reading in OET? score a c+ 330 and I need a 350.
What is my chance?
There is little possibility as the reading test is objective in nature. It’s better to book another exam and practice these tests: OET Reading Practice
Hello I got B in listening,reading and writing but C+ in speaking.
What should i do??
Use this service to ensure B next time: OET Speaking Practice
I given for remarking writing 320 and speaking 310.any chance to upgrade score or not.
Yes,Watch this video
Hi! How many correct items do I need to have for me to get a B grade in reading? Is it 28 or 30? I’m quite confused with the previous comments. Thank you in advance.
Updated number is 30, and even this is not fixed as for a very difficult exam 350 can be achieved for 28 marks as well. So, the numbers are more or less approximation and not exact.
How to calculate score
Hai.. while attempting 2nd time, whether we have to attend all modules or attend the module which is having low score
Yes, all 4 modules need to be taken again. Before booking another exam, do confirm with the your registration authority.
I got 360 in listening ,370 in reading and speaking. 260 in writing .can I go for remarking?is there any chance to get 300 after remarking?
Hello! Do you lose marks for not being able to complete the task in writing? I missed to include a brief history but was able to finish the letter.
you may lose marks for case notes selection but you did good by finishing the letter.
I’ve got results today. I got 350 and above in 3 skills except listening in which the score is 340. As I’m a doctor I need 350 in each right? Is there any possibility to contact GMC and request regarding my score
So, sorry to know you lost by 10 marks in the listening module. Not sure if GMC would make an exception in your case but it’s up to you but there’s no harm in trying your luck by sending them an email.
I have got speaking 340 and other modules 370.so is there any chance to get 350 if I go for remarking?
Yes, if you can wait, then it makes sense to give remarking a try
I got writing 290 can I apply for revaluation or resit
if you can afford, go for both. Otherwise, resitting would be a better option.
I got 330 in reading and listening 280 in writing.Is there any hope for remarking?
Nope. Book another one.
I have scored 400 in listening ,370 in reading and writing but 340 in speaking. What should I do now?? Do I have to take entire test again??
Yes, but you can still contact your registration body to confirm.
I got band B in reading listening and writing,but c+ in speaking.. what should I do now??
If you are confident that you deserved B grade, then go for reevaluation. Alternatively, book another OET exam.
Can anyone answer these two questions?
I had 320 in my writing subtest on 7/3/2020, is there any success story of getting 350 after re-marking?
And the 1 million question, how the OET change the mark to scale, I mean what is the mark that I should have to get 350 on the scale????
Hi, yes, there is a possibility of score going up post-reevaluation. Your other query will be answered soon by an expert.
What will be my grade if I have scored 51/63 in writing module
OET does not calculate score that way. In order to achieve 350 or a B grade, a letter should predominantly have at least 5 in all criteria and 2 in purpose.
percentage of questions to get right for getting A in the test
39 out of 42
In order to get 400 in writing, how much out of 38 should I score? I mean in each of the new writing criteria!
Is it really difficult to get 400 in each section in a single sitting ? 3 months of preparation is enough for that ?
hi sir,
can u please guide how we calculate writing score.
hai, i got A for speaking and listening , B for reading ,but 300- C+ for writing. Will I get a B grade if I go for revaluation ?
I can’t answer whether you will get 350 after reevaluation or not. If you are convinced that you deserved 350, then of course go for reevaluation. Otherwise, book another exam and start preparing.
Hi! I could not finish the oet writing task, I just ran out of time. I could not conclude my letter. Does this mean it’s straight c? Is there any chance of getting b?
If l score 320 in reading, how many correct answers. In calculator 27 it is 310 and 28 it is 330.
The calculator is approximation only.
Please let me know I can works as Registered Nurse for UK my OET Result Speaking B, Listening C+, Reading C+ & Writing C
My result today with listening 330, reading 320, writing 360 and listening 350. How many questions are wrong in listening and reading according to given score?please guide.
Are they going to consider mispelled answers? What if it should be plural like sores but i answered sore,will they consider?
Yes, in both cases, as long as the meaning remains unaltered.
I have scored 340 in reading and pass oter 3 subset. Does remarking hep?
No
I took my oet in Nov 21 and the results came out Dec 10 and these are my scores: L-380, S-360, R-370 and W-290. But I requested for remarking in writing because I was sure of what I wrote. Fortunately by God’s grace the remarking result came out 24 Dec and the grade changed from 290 to 350.
So I am encouraging anyone to go for remarking especially for writing if you are sure of what you wrote in the exam.
Wishing people yet to take the exam success in all sections.
I have done my previous exam on 12/12/2020 and result published on 20/1/2021 .next exam date on 12/6/2021 whether I can do clubbing on thz duration???
Got 320 in listening, 330 in speaking and 330 in speaking. Should I go for remarking.
i got my results today. i scored 390 in listening, 360 in speaking, 370 in writing and 340 in reading. will a remarking help?
Hi I got my results today and I got Reading 380, listening 370, writing 360 and speaking 340. I also applied for a remark for speaking today 13 may 2021. Please when will my final remark results come out ?
whats the score of usa
In my 1st attempt i got Reading 350, listening 360, writing 350 and speaking 290., On my 2nd attempt i got Reading 330, listening 350, writing 300 and speaking 350, Can i club this result for New Zealand
Hi,
I have c+ in all modules exM dated 06February 2021
And B score except reading modlue in 26th may exam.
Can you pls advice the clubbing options are possible for any countries like UK OR IRELAND
Hi. I would like to ask.
I got 1st test: L-C+, R-C+, W-B, S-B and 2nd test: L-B, R-B, W-C+,S-C+. Can i do clubbing for this two results?
Hoping for you response. Thank you
Informative article
I scored a grade B in writing, speaking ,reading and a grade C+ in listening.
Please,is this result useful?
Please, can I combine the following results?
24.07.21
Listening-330 (С+)
Reading-370(B)
Writing-300(C+)
Speaking-360(B)
07.08.21
Listening-360(B)
Reading-330(C+)
Writing-320(C+)
Speaking-360(B)
OET computer based at venue meaning writing, listening and reading at venue? How about Speaking? Venue or home? thanks
What is the possibility of getting 300 score in my writing if I ask for remarking for my writing scored 290? I want to take a chance to get a C+, to add in my score “B” for the rest of the subtest.. thank you in advance for a reply
Hi Vita, did NMC accept your combined score, because I have got similar results?
Thanks,
Silviu
hi how can I improve my reading?
i had in novemebr my first time OET exam,which i got 390 speaking, 350 writing, reading 210 and listening 250 . i booked for decemebt 18th . In addition i am a doctor and live in Australia. which score do i need to get in this time to pass my exam
This Blog is helpful.
280 marks in oet reading means how many marks i got it out of 42